Clinical Examination of Respiratory System
Clinical Examination of Respiratory System
Respiratory system is a ventilator system that keeps us alive to breath everyday.It is very important to keep all our systems of our body in good condition.Clinical examination of Respiratory System gives us an idea about how our respiratory system is actually working based on various aspects.
Before we go through clinical examination we need to know anatomy of respiratory system.

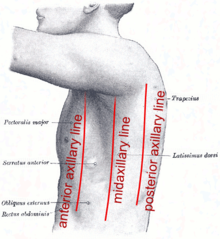
Mid sternal line
Mid clavicular line
Anterior and Posterior axillary lines
Mid axillary line
Mid spinal line and Mid scapular line
What do i need to do before examination?
Wash hands
Introduce yourself
Confirm patient's details(Name and Date of birth)
Explain about examination in detail
Ask and gain for consent
Expose the patient's chest
Position patient at 45 degree
Before starting ask if the patient feels any pain
What is the method of examination?
General Examination
Cyanosis,Shortness of breath,cough,wheeze,stridor and cachexia.
1.Hands
Peripherial cyanosis
2.Temperature
Coldness which indicates that there is poor perfusion or vasoconstriction
3. Bruising or thinning skin
Due to long term steroid use

4.Tar staining
Due to smoking
5.Tremors
Flapping tremors
Due to Asterixis-CO2 retention

Fine tremors
Due to beta-agonist use(salbutanol)

6.Clubbing test
Schamroth's window test-lost when finger clubbing

7.Tongue
Central cyanosis
Bluish discoloration of lips and mucous membrane
It is located between two heads of sternocleidomastoid. It is raised in cor pulmonale
10.Examination of chest
There are four methods,
1.Inspection:You only look at patient without touching or palpating the patient and look for bad condition or deformities

1.Shape of chest
Check for any chest deformations and scars.
Scars:
Central chest: Sternotomy and Thoracotomy
Mid Axillary: Chest drain
Clavicular: Pacemaker
 2.Symmetry of chest
2.Symmetry of chest
Bilaterally symmetrical and elliptical in cross section
3.Movement of chest
Symmetrical movement of chest when patient inspires and expires
4.Respiratory movement
Respiratory rate:12-20 breaths/min is normal
Tacypnea: Abnormal rapid breathing
Bradypnea: Abnormal slow breathing
Cheyne-Stokes respiration
Kussmaul breathing
2. Palpation:Method of feeling with the fingers or hands.
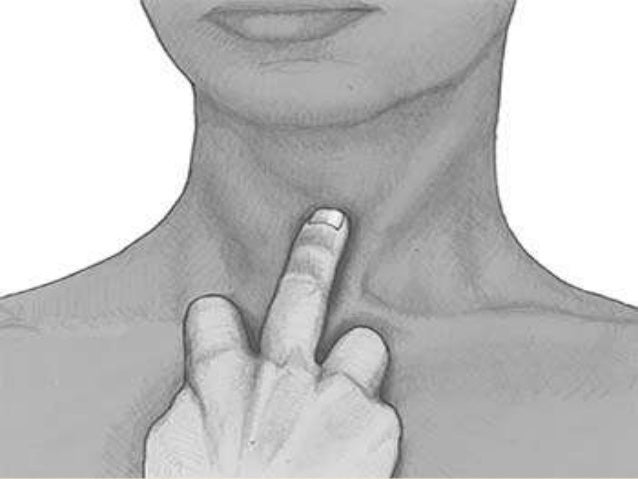
1. Tracheal Position
Tracheal diversion is most common in Pneumothrox.
Normal cricosternal distance is 3-4 fingers
2.Palpate Apex Beat
Mid clavicular line at 5th intercostal space

3.Palpate Lymph Nodes
Lymphadenopathy causes
Sarcoidosis
Infection
Malignancy
4.Expansion of chest
Reduced chest expansion when lung collapse and pneumonia.
Should be done on both anterior and posterior; upper and lower parts of chest and compare.


3.Percussion: Method of tapping body parts with fingers or hands .It indicates the presence of fluid or not in chest.

1. Percuss the lung fields
It should be done on both sides of chest anterior and posterior and even axial region.
Resonant percussion-Normal
Hyper Resonant-Pneumothorax
Dull percussion- Abnormal
Consolidation
Collapse
Effusion
Stony Dullness-Pleural Effusion
Note:Cardiac Dullness
Anterior

Posterior

4.Auscultation: Listening to internal sounds of body using a stethoscope.
1.Positions of auscultation
Anterior
 Posterior
Posterior 1.Vesicular breathing
Normal breath sound
2.Inspiratory stridor
Upper airway obstruction
3. Wheez
Asthma and COPD
4.Fine Crackles
Pulmonary fibrosis
5.Coarse Crackles
Pneumonia and Pulmonary Edema
2.Vocal Fremitus
Ask the patient to tell a number or letter when stethoscope placed on chest.
Increased Vocal Fremitus
Consolidation
Lobar collapse
Tumor
Decreased Vocal Fremitus
Pleural Effusion
Additional
Sacral Edema
Pedal Edema(Right Ventricular Edema)
After Examination
Thank the patient
Wash Hands
Note:Examination should be done on both sides of chest anterior, posterior and lateral axilla region.
This completes the Clinical Examination of Respiratory System
I hope I was able to give an view on Clinical Examination of Respiratory System.





Comments
Post a Comment